Entourage Effect: Experience a Full Spectrum High
In recent years, cannabis enthusiasts and researchers alike have come to understand the unique harmony of cannabinoids and terpenes in cannabis plants. These compounds individually provide a range of effects, but it's the entourage effect that enhances their potential, leading to a more fulfilling and comprehensive experience. What exactly is the entourage effect? Well, let’s take a look at this cannabis term and find out just what determines this phenomenal experience.
What is the Entourage Effect?
The entourage effect refers to the synergistic interaction between cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids in cannabis. Individually, these compounds have unique effects, but when combined, they work together to create a more potent and nuanced experience. This concept is the basis of the preference for full-spectrum cannabis products, which contain a wide range of these compounds to maximize the entourage effect.
What Does a Full Spectrum High Feel Like?
A full-spectrum high is often described as a more comprehensive and well-rounded experience compared to isolates or distillates (more on that later). Users report feeling the full range of effects that cannabis has to offer, both physically and mentally. This may include a sense of relaxation and calm, mental clarity, and increased focus, as well as potential pain relief and anti-inflammatory benefits.
In essence, a full-spectrum high can be characterized as a "mind-melt" and a "full-body" sensation, providing an elevated experience that goes beyond the effects of single cannabinoids or terpenes. The entourage effect ensures that users can enjoy the full potential of cannabis, with a more balanced and harmonious outcome. It tends to last longer and provide a more satisfying experience overall.
Full Spectrum vs Broad Spectrum vs Distillate vs Isolate
To achieve a full spectrum high that engages the entourage effect, you must either smoke high-quality cannabis flower or a full spectrum extract. When you smoke quality cannabis, it already contains all its natural components, so you can trust that you’re experiencing a full spectrum high.
But when it comes to extracts, what happens in the lab plays a big role in the end products. For example, a full spectrum extract was created with plant preservation in mind. Of course, the fats and waxes are stripped, and the extraction process is solely focused on retaining the highest possible concentration of terpenes, cannabinoids, and flavonoids.
Examples of full-spectrum extracts include live resin, rosin, live rosin, budder, crumble, and several other formats. The idea is that the end product contains a large volume of these precious compounds to deliver a robust entourage effect.
So, if it isn’t full spectrum, what is it? The next step in the extraction process produces what is known as broad-spectrum extract. This type of cannabis concentrate includes a range of cannabinoids and terpenes but typically lacks THC, offering a similar experience without psychoactive effects. What’s the point, you might ask? Broad spectrum products are more common in the CBD market, where someone might want the therapeutic benefits of cannabis but can’t consume THC. This is the case for people who have government jobs or face regular drug testing.
Next in the chain of cannabis extracts is distillate, which has become incredibly popular in the cannabis industry for its extreme THC potency. Some distillates can achieve nearly 99% THC. But as we are learning, potency isn’t just about THC. Distillate is void of terpenes and contains primarily THC (or whichever cannabinoid is desired). It lacks color or flavor, and when used in vape pens, it’s typically mixed with plant-derived terpenes to add back what was lost in extraction.
Last, we have isolate, which is just what it sounds like: an isolated cannabinoid. This is a pure, often crystalline version of a cannabinoid, and it contains no other compounds. Isolated THC is 100% pure, with no terpenes or remnants of any other cannabinoids. While isolate will get you very high, it is short-lived and does not come with the full spectrum experience like the entourage effect.
Components of the Entourage Effect
Okay, so now that we know the entourage effect is a culmination of cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids, let’s look at some of the most common components in each of these categories.
Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids are naturally occurring compounds found in cannabis plants, and they are actually called phytocannabinoids. The human body also produces cannabinoids, and these are called endocannabinoids. We commonly refer to both of these as simply cannabinoids. The most well-known cannabinoids are tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), which we all know and love for their psychoactive and therapeutic effects, respectively.
However, there are over 100 different cannabinoids present in cannabis, each with its unique characteristics and potential benefits. Here are a few others you’ve likely experienced in a full-spectrum cannabis product.
Cannabigerol (CBG): Often referred to as the "mother of all cannabinoids," CBG is a precursor to THC, CBD, and CBC. As a non-intoxicating compound, it may have potential benefits such as anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antibacterial properties. Some studies suggest it could also be effective in reducing intraocular pressure, making it useful for glaucoma treatment.
Cannabinol (CBN): CBN is formed when THC degrades over time, and it is mildly psychoactive. It has gained attention for its sedative effects, making it potentially beneficial for individuals with sleep disorders. Additionally, CBN may exhibit anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and anticonvulsant properties.
Cannabichromene (CBC): Although non-intoxicating, CBC may have various potential therapeutic benefits. Research suggests it could have anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antidepressant properties. Additionally, CBC may promote neurogenesis (the growth of new brain cells) and demonstrate antimicrobial and antifungal effects.
Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV): THCV is structurally similar to THC but has different effects. It is known for its potential appetite-suppressing properties, making it a potential candidate for weight management. Furthermore, it may exhibit anticonvulsant, neuroprotective, and anti-inflammatory effects, making it potentially beneficial for conditions such as epilepsy, Parkinson's disease, and multiple sclerosis.
These lesser-known cannabinoids, along with the more prominent THC and CBD, contribute to the overall effects and therapeutic potential of cannabis. As research continues to uncover the unique properties of these compounds, our understanding of their individual and combined benefits will expand, paving the way for new and innovative cannabis-based therapies.
For now, the best way to learn more about what you’re consuming is to ask your budtender for lab results, or check out the brand’s website. The certificate of analysis not only shows the purity and quality of the product but it gives excellent insight into the comprehensive list of cannabinoids and terpenes in each flower or extract.
Terpenes
The diverse world of cannabis terpenes encompasses a wide variety of aromatic compounds, each with its unique scent, flavor, and potential effects. There are potentially hundreds of terpenes in cannabis, but lab testing has not evolved far enough to find them all just yet. For now, we see a solid handful of the more dominant terpene contributing to the entourage effect.
Myrcene: As the most abundant terpene in cannabis, myrcene has an earthy, musky aroma reminiscent of cloves. It is known for its potential relaxation and sedative effects, and it may also exhibit anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties.
Limonene: With its distinct citrusy scent, limonene is the second most common terpene in cannabis plants. It has been associated with uplifting and stress-relieving effects, as well as potential anti-anxiety, antidepressant, and anti-inflammatory properties.
Linalool: Recognizable for its sweet, floral aroma, linalool is found in various plants, including lavender. It is thought to have calming and sedative effects and may also have potential anxiolytic, antidepressant, and neuroprotective properties.
Caryophyllene: Exhibiting a spicy, peppery aroma, caryophyllene is unique among terpenes, as it can also act as a cannabinoid, binding to CB2 receptors in the endocannabinoid system. This interaction may contribute to its potential anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and anti-anxiety effects.
Pinene: As the name suggests, pinene has a strong pine aroma and is found in various coniferous trees. It is known for its potential bronchodilatory, anti-inflammatory, and analgesic effects, and it may also help counteract some of the short-term memory impairment associated with THC.
Nerolidol: This lesser-known terpene has a woody, floral, sweet smell reminiscent of apples or roses. When consumed in cannabis, nerolidol offers a sedative effect with anti-anxiety properties.
Terpinolene: Exhibiting a complex aroma that combines notes of pine, citrus, and floral, terpinolene is less abundant in cannabis but still plays a role in its overall profile. It is thought to have potential sedative, antioxidant, and antimicrobial properties.
Humulene: Present in hops and cannabis, humulene gives off a woody, earthy scent. It may exhibit anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties, and some research suggests it could have potential appetite-suppressing effects.
These terpenes commingle to create the characteristic and complex flavor and aroma we love from cannabis. There is nothing quite like this symphony of scents, and the accompanying effects leave us wanting more with every hit. When combined with cannabinoids, they play an essential role in the entourage effect, offering a more comprehensive and nuanced experience for cannabis users.
Flavonoids
Flavonoids are a group of phytonutrients that are found in many plants, including cannabis. These compounds have been found to have various therapeutic properties and may play a role in the overall effects of cannabis. There are over 20 flavonoids that have been identified in cannabis, but these four show up pretty often.
Apigenin: This flavonoid is found in many plants, including chamomile, parsley, and cannabis. It has been found to have anti-inflammatory, anti-anxiety, and anti-cancer effects. Apigenin may also have neuroprotective properties and has been studied as a potential treatment for Alzheimer's disease.
Vitexin: Vitexin is another flavonoid found in cannabis, as well as in passionflower and other plants. It has been found to have anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer effects. Vitexin may also have neuroprotective properties and has been studied as a potential treatment for Parkinson's disease.
Cannaflavin: Cannaflavin A and B are flavonoids that are unique to cannabis. They have been found to have anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving effects that are more potent than those of aspirin. Cannaflavins may also have anti-cancer properties and have been studied as a potential treatment for colon cancer.
Anthocyanins: Anthocyanins have been found to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. They may also have neuroprotective properties and have been studied as a potential treatment for various neurological disorders.
Fun fact: flavonoids not only contribute to flavor and effect, but they are also one of the magical ingredients that give cannabis its color. From red to purple, green, and yellow, flavonoids are responsible for the beautiful color palette we see from different strains.
What is the Endocannabinoid System?
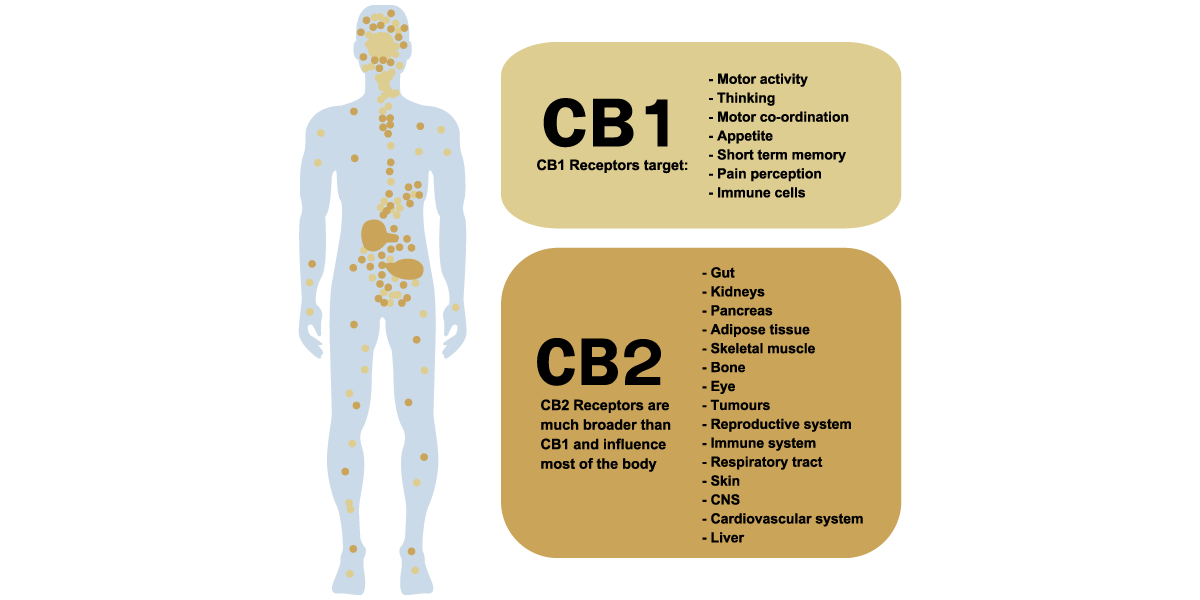
The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is a complex network of receptors and neurotransmitters that exist throughout our body and play a vital role in regulating various physiological processes such as appetite, pain sensation, mood, memory, and immune function. The ECS is made up of two primary receptors: CB1 and CB2 receptors, which are primarily found in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and immune system, respectively.
Cannabinoids interact with the CB1 and CB2 receptors in the ECS to modulate the release of neurotransmitters that regulate various physiological processes. Terpenes and flavonoids, when ingested or inhaled, enter the bloodstream and bind to the CB1 and CB2 receptors. The specific effects of these compounds depend on a variety of factors, such as the specific cannabinoid or terpene, the dose, and the individual's physiology.
Terpene + Cannabinoid Pairings
Combining specific terpenes and cannabinoids can help target certain effects and enhance the overall experience for cannabis users. So if you’re looking for an entourage effect that is focused on specific moods, effects, or benefits, seek out some of these combinations.
Relaxation and Stress Relief
Cannabinoids: CBD, CBN
Terpenes: Myrcene, Linalool, Limonene
Pain Relief and Inflammation Reduction
Cannabinoids: CBD, THC, CBG, CBC
Terpenes: Myrcene, Caryophyllene, Pinene, Humulene
Energy and Focus
Cannabinoids: THC, THCV
Terpenes: Pinene, Limonene, Terpinolene
Sleep and Relaxation
Cannabinoids: CBN, THC, CBD
Terpenes: Myrcene, Linalool, Terpinolene
Mood Enhancement and Stress Relief
Cannabinoids: CBD, THC
Terpenes: Limonene, Linalool, Pinene
Appetite Stimulation
Cannabinoids: THC, CBD
Terpenes: Humulene, Myrcene, Caryophyllene
Keep in mind that individual reactions to cannabinoids and terpenes may vary, so it is essential to experiment with different strains and combinations to find the most suitable and effective blend for your specific needs. Keep a journal! Log what you try and how it makes you feel. Soon, you’ll have a cannabis report card with prescriptions perfectly tailored to how your ECS responds to different cannabinoid and terpene profiles.
Experience the Entourage Effect with Cream of the Crop
The entourage effect highlights the importance of preserving the natural composition of cannabinoids and terpenes in cannabis products. Full-spectrum extracts offer users an enriched experience that harnesses the synergy between these compounds, delivering a more profound and personalized high. As our understanding of the entourage effect and the complex interplay of cannabinoids and terpenes continues to grow, so does the potential for discovering new ways to enhance and tailor the cannabis experience to meet individual needs and preferences.
Are you ready to experience a full-spectrum high? Head on over to our shop and explore our collection of full-spectrum extracts and supreme quality flower.